Key Takeaways
- Optical prisms are versatile glass components used to manipulate light in various applications, from laser alignment to microscopy.
- This optical prism selection guide outlines key prism geometries, such as right-angle, roof, and equilateral prisms, and their primary functions, including deviation, inversion, and dispersion. It highlights applications in fields like spectroscopy, medical imaging, and satellite communication.
- Additionally, the guide discusses the importance of substrate selection based on light wavelengths and environmental conditions. Avantier offers a variety of prism options for diverse optical needs, ensuring precision and efficiency.
Optical Prisms Selection Guide
Optical prisms are solid glass optical components that can be used to manipulate light in many ways. From the minuscule dove prism in an endoscope to the porro prism in a space telescope, prisms can be found in many widely varying optical systems. Chosen wisely they can lead to more efficient, compact design and higher image quality. But just how do prisms work, and what prism is best for your application?
This selection guide will provide an overview of the different geometries you may see in prisms, complete with details about prime applications and key functionalities. Knowing whether you need dispersion, deviation, displacement or rotation will help you decide what prism type is best for you.
You should also be aware that prisms can be made of various substrates, and the substrate that is best for you will depend on the specific wavelengths of light you are targeting and the environmental conditions in which you work.
Your Selection Guide to Optical Prisms
Right Angle Prism
A right angle prism is the basic geometry you probably think of when you think of a prism— a neat triangle wedge that deviates a ray path by 90°. These prisms are also called 45° – 90° – 45° prisms. 45° – 90° – 45° prisms are often used in combination to displace an image or beam.
The standard way to use a right-angle prism is with light entering through one leg and exiting through another. The image you get is left-handed. But if you change the orientation relative to the incident beam so that light enters through the hypotenuse, your prism is called a porro prism. The light will bounce against both legs and exit through the same side, the hypotenuse. This results in a right-handed image.
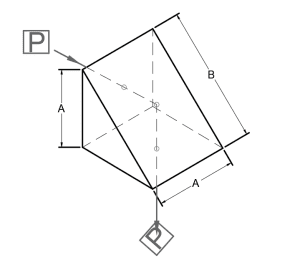
Applications of right angle prisms include:
- Laser Alignment
- Medical Instrumentation
- Telescopes
- Microscopy
- Endoscopy
Primary Functions: Deviation and Displacement
Roof prism
A roof prism looks like the roof of a house, just the way you might have drawn it back in elementary school. Total internal reflection on the ‘roof’ enables this prism to bend light by 90 degrees even while inverting it. There are a number of types of roof prisms, each with slightly different geometries; one common type is the amici roof prism. The amici roof prism gives a right handed image.
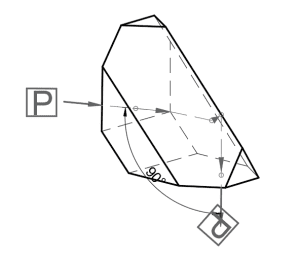
Applications of roof prisms include:
- Spotting scopes
- Microscopes
- Telescope Eyepieces
- Binoculars
Primary Functions: Deviation and Inversion
Equilateral prism
If you think of a prism as a bit of glass that turns light into rainbows, you’re thinking of an equilateral prism. An equilateral prism will have three 60 degree angles and is used primarily to disperse light into its primary colors.
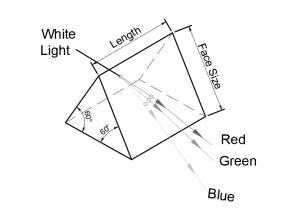
Applications of equilateral prisms include;
- Spectroscopy
- Telecommunications
- Laser light separation
Primary Functions: Dispersing light into its component wavelengths.
Dove Prism
There are two kinds of dove prisms; one with a reflective coating and one without. The uncoated version rotates a prism by twice the prism rotation angle and produces a left handed image. The coated version reflects a beam back onto itself, and produces a right handed image.
Both types of dove prism look the same; like a right angle prism with one corner truncated or cut off.
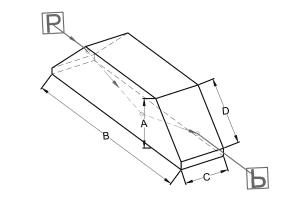
Applications of dove prisms include;
- Imaging around corners
- Interferometry
- Medical imagery
- Astronomy
Primary Functions: Rotation, inversion, retroflection.
Penta Prisms
A pentaprism, as its name suggests, has five faces. Two of these faces are at a ninety-degree angle to each other, and when incident light enters one of these faces it will emerge from the other, having been deviated 90°. Since the image is neither inverted nor reversed, these prisms are a favorite choice for many imaging applications.
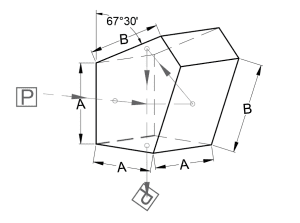
Applications of penta prisms:
- Display systems
- Plumb level and surveying
- Spectroscopy
- Metrology equipment
- Projection
- Visual targeting
- Cinephotography
Primary function: Deviation
Retroreflectors
Retroreflectors are also called trihedral prisms or corner cube reflectors; they reflect any beam that enters the prism face and sends it back at an 180 degree angle. The image resulting from a retroreflector is left handed.
Retroreflectors have many applications, and they aren’t all earth-bound. When the Apollo 11, 14, and 15 landed on the moon, the astronauts left retroreflectors behind. Scientists on Earth aimed lasers at the prisms and, through time of flight calculations, were able to calculate precisely the Moon’s orbit and shape.
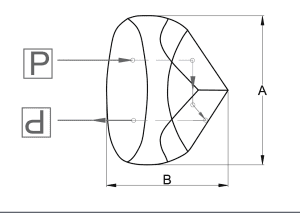
Applications of retroreflectors:
- Satellite communication
- Laser tracking
- Precise alignment
- Rangefinding
- Free space optical communications
- Boresighting
- Interferometry
Primary function: Deviation and displacement
Light Pipe Homogenizing Rods
Light pipe homogenizing rods are a special kind of prism that hardly looks like a prism at all. And rather than scatter light, these prisms make it tidier—- more homogenized. These square or hexagonal pipe-shaped prisms are also known as waveguides, light funnels, homogenizing rods or light guides.
Light enters a waveguide through one end, and is kept within the prism with total internal reflection till it is emitted at the other end. These light funnels are often used to transform the light from non-uniform sources into clear, homogenized light.
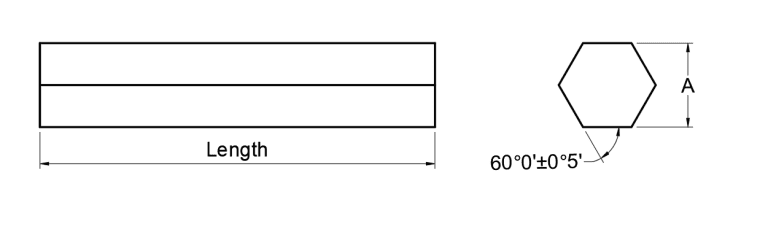
Applications of light pipe homogenizing rods:
- Micro-Projectors
- CPV optical rods
- OEM Illumination
- LED Illumination
- Laser Speckle Reducers
- Lithography
Primary function: Homogenization of Light, Direction of Light
Microprisms
A micro prism is a very small prism, often no more than 0.1-5mm in size. These prisms provide precise manipulation of light in a very small package, and may be used with optical fibers or other micro-optic systems.
Microprisms are available in many of the geometries discussed above, including dove prisms, right angle prisms, and penta prisms.
Applications of micro prisms include:
- Optical fiber communications
- Advanced camera technology
- Medical instrumentation
- Industry & Research
- Micro-optic Assemblies
Primary function: Rotation, Inversion, Diversion, Displacement and Direction of Light
Optical Prisms at Avantier
This is only a brief survey of some of the more common optical prism designs, and not a comprehensive look at all the options out there. Avantier is at the forefront of prism manufacturing, and we offer custom design services for any optical system you might need. Whether you’d like to put in a custom order, Contact us today.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!