UV Lenses
Ultraviolet (UV) light, with wavelengths ranging from 10 nm to 400 nm, falls between visible light and X-rays on the electromagnetic spectrum. UV lenses are special optical lenses designed to be used for light with wavelengths lower than 400 nm. They may be used for laser applications that extend into the UV spectrum, in focusing applications, or in collimation. At Avantier, we produce custom UV lenses upon request.
Depending on the design of the lens and the substrates used, a UV lens may perform optimally over a larger band than simply the UV range. UV-fused silica lenses can be designed to have strong performance in the visible (VIS), near-infrared (NIR), or infrared (IR) spectra as well as over the UV range.
Applications of UV Lenses
UV lenses may be used for focusing ultraviolet light sources, for polychromatic illumination in fluorescence applications, for microlithography, spectroscopy, and laser fusion projects. From military and defense to industrial quality control and forensics, UV optics is a robust and rapidly growing field.
Sometimes the term “UV lenses” is also used to refer to lenses that are UV-coated to protect the eye from the sun’s harmful rays. Macular degeneration is just one of many eye problems that can occur if the eye is subjected to UV rays from light sources like the sun. However, UV protection coatings can ensure that you are fully protecting your eyes, even when the ultraviolet index is high.
Special Considerations for UV Lenses
While UV lenses function similarly to other lenses and are used in similar applications, there are important considerations when working with UV optics. Scattering, dispersion effects, and laser damage/degradation are crucial issues to consider when designing a UV setup.
Scattering effects occur across the entire spectrum, but encountering any inhomogeneities or scratches on a lens. To minimize scattering, ensure that any UV lens has minimal parasitic birefringence, a homogeneous refractive index, and a highly polished surface.
Dispersion effects also vary depending on the spectral region, with many substrates exhibiting stronger chromatic dispersion in the UV range compared to visible (Vis) and infrared (IR) light. Achromatic optics can mitigate this issue when necessary.
Laser damage and degradation can be a concern, as the optical damage threshold of substrates is often lower in the UV spectral range than for longer wavelengths. This is due to two-photon absorption, which can be sufficient to bridge the band gap. To prevent laser damage and degradation, ensure your UV lens is designed for UV light and lasers, and avoid exposing it to vapors from lubrication oils within intense ultraviolet beams.
Examples of UV Lenses
A few examples of standard UV lenses that can be custom ordered to various focal lengths include:
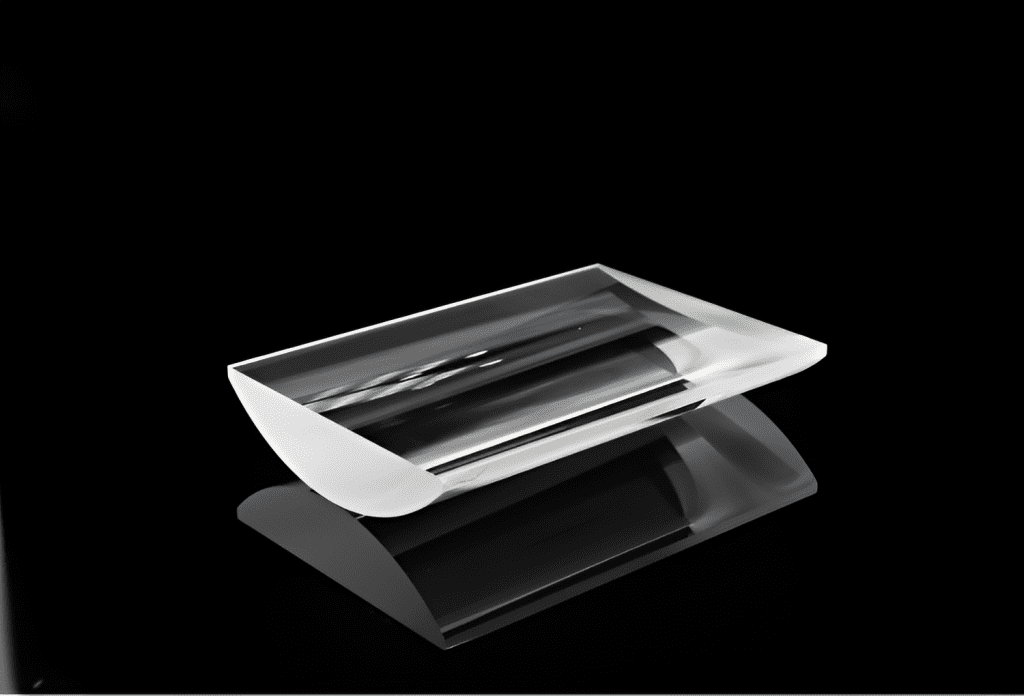
- Achromatic lenses
- Aspheric lenses
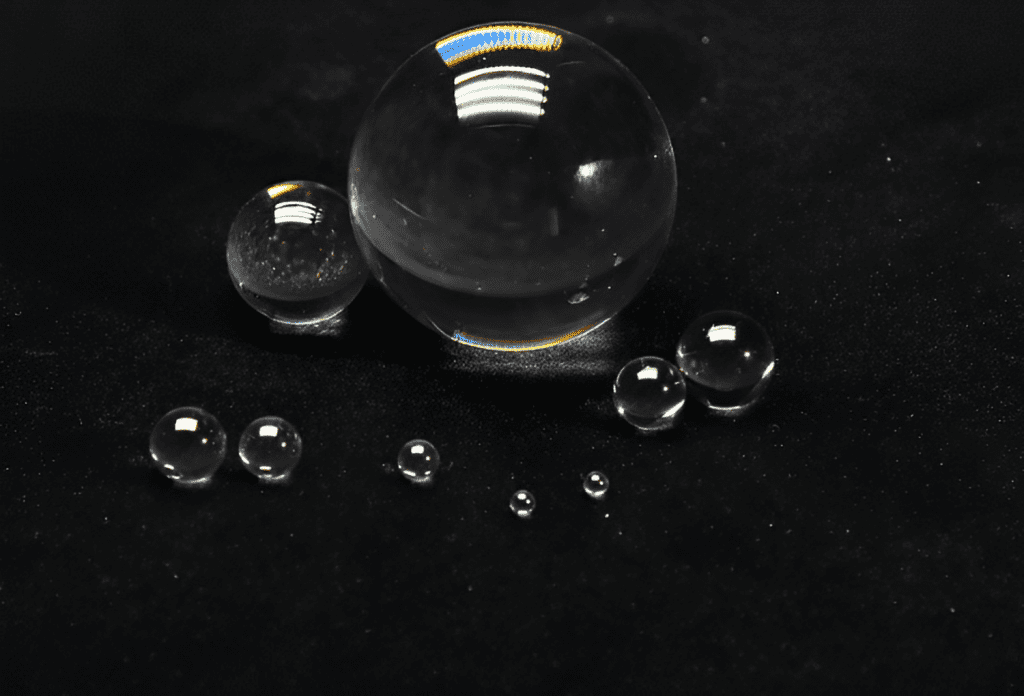
- Ball lenses with spherical surfaces
- Singlet lenses (plano convex lenses PCX or double convex DCX lenses)
- UV-to-NIR corrected triplet lenses
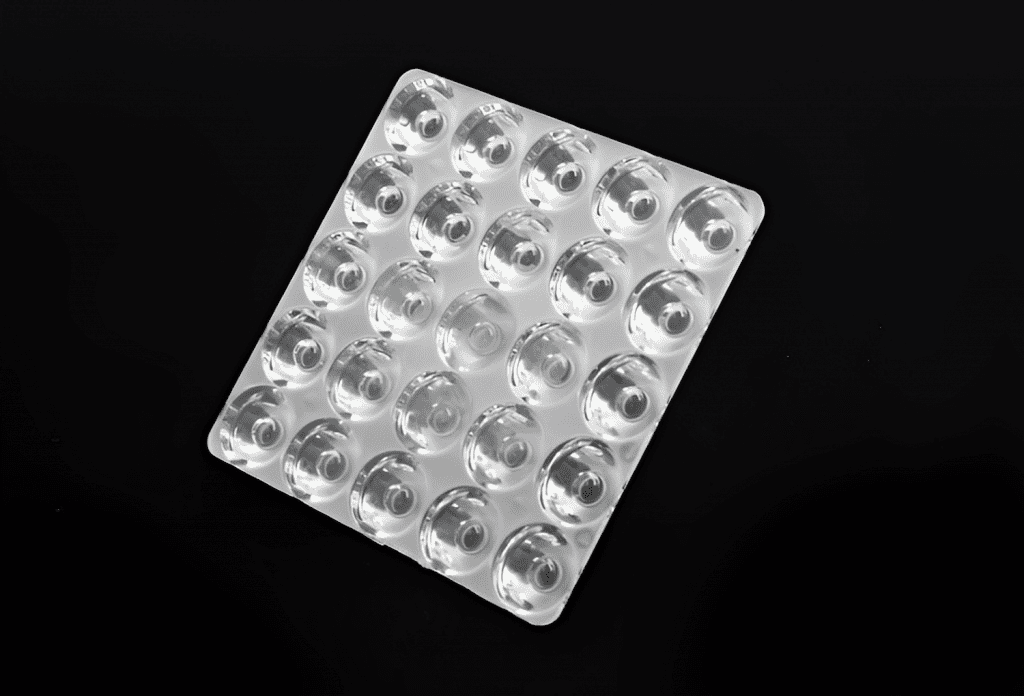
- Microlens arrays and lens kits
- Cylindrical microlens arrays



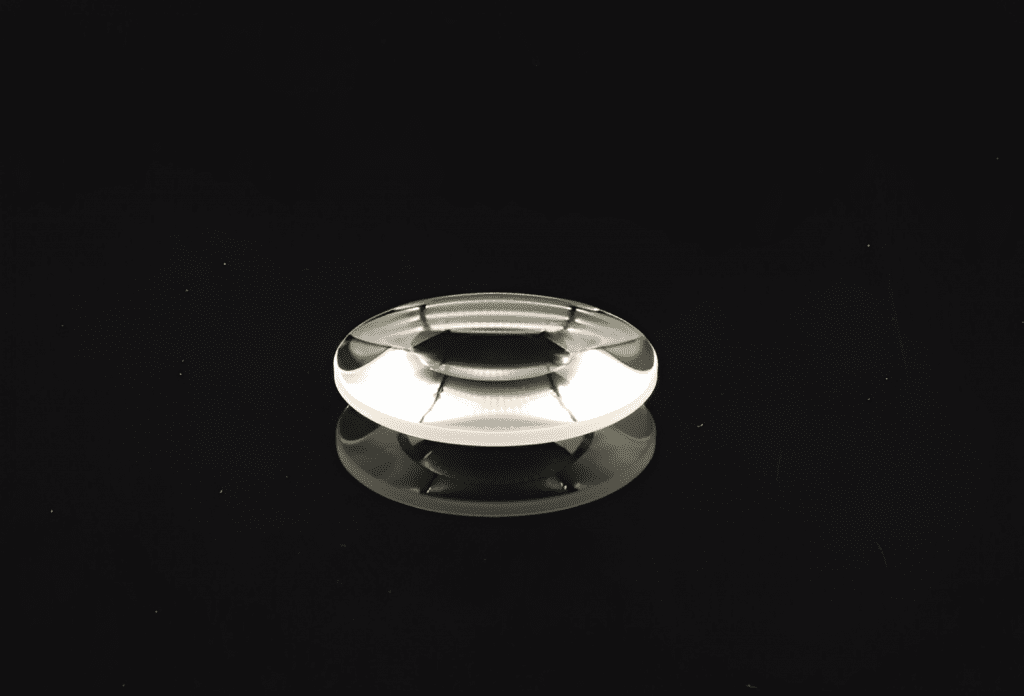


Specifications
Diameter Range | 10-50mm |
Diameter Tolerance | +0/-0.1mm |
Thickness Tolerance | +/-0.1mm |
Surface Quality | 60-40 S-D |
Power(Irregularity) | 3(0.5)fringes |
Centering Tolerance | <3′ |
Clear Aperture | 90% |
Our optical engineers are not only highly skilled at producing quality custom designs, they also are renowned for their interpersonal skills and their ability to work with a wide range of clients, providing a customized experience to every person we serve. Whether you need a lens designed for infinite conjugate applications or a UV finite conjugate lens for a videography application, we can get you what you need. Contact us today to schedule an initial consultation.
WE CAN HELP YOU!
Contact us NOW for sales & expert advice.