Achromatic Lenses
The achromatic lens is an important optical component that offers excellent correction for both chromatic and spherical aberrations, which often occur in optical systems with traditional lenses. Chromatic aberrations occur due to the dispersion of light, where different wavelengths bend at varying angles while passing through an optical element. This results in non-coinciding focal points for different colors of light, causing blurred or color-fringed images. Chromatic aberration is particularly noticeable in traditional lenses, where the refractive index of the material causes light to bend differently based on its wavelength. This phenomenon can hinder the imaging capabilities of optical systems, impacting industries like photography, microscopy, and astronomy in which image clarity and quality are paramount.
Avantier offers computer-designated achromatic lenses that minimizes spherical aberration and coma for smaller focused spot sizes at infinite conjugate ratios.
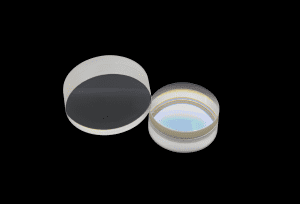



Achromatic lenses address chromatic aberrations by combining multiple lens elements with different dispersive properties. This combination ensures that various wavelengths of light converge at a single focal point, reducing color fringing and enhancing image quality. Typically, an achromatic lens consists of two elements: a positive (convex) lens made from low dispersion glass like crown glass, and a negative (concave) lens made from high dispersion glass like flint glass. This pairing effectively cancels out chromatic aberration, leading to clearer images and better color accuracy.
Since the number of elements does not correlate with the number of rays it corrects, for example, an achromatic lens designed for visible wavelengths corrects for red and blue regardless of whether it is a doublet or triplet.
Achromatic Lenses Applications
- Photography and Imaging: They are commonly used in cameras, camcorders, and telescopes to ensure sharp and accurate imaging, free from color fringing and distortion.
- Microscopy: They are vital components in microscopes, enabling researchers to observe microscopic samples with exceptional clarity and accurate color representation.
- Medical Instruments: They play a crucial role in medical instruments such as endoscopes and ophthalmoscopes by ensuring accurate visualization and diagnosis.
- Laser Systems: They are employed in laser systems to improve beam quality and enable precise focusing of laser beams.
By carefully combining lens elements with different dispersion properties, achromatic lenses offer exceptional image quality, improved color accuracy, and enhanced optical performance across a wide range of applications. As technology advances, achromatic lenses will continue to be a cornerstone of precision optics, driving new frontiers in imaging, research, and industrial applications.
Materials
- Optical glass, UV fused silica (JGS1), infrared fused silica (JGS3) and calcium fluoride (CaF2), Barium fluoride (BaF2) and other crystalline material
Manufacturing Capabilities
Specifications | Factory Standards | Manufacturing Limit |
Dimension Tolerance | +/-0.03mm | +/-0.01mm |
Center Thickness Tolerance | +/-0.03 mm | +/-0.02mm |
Radius Tolerance | +/-0.3% | +/-0.2% |
Surface Quality(S/D) | 20-10 | 10-5 |
Irregularity | 1/5 Lambda | < 1/10 Lambda |
Centration(arc min) | 3′ | 1′ |
Avantier Inc. offers achromatic lenses as custom optical components that can be manufactured according to different lens designs and varying needs across a broad spectrum of wavelength ranges, including visible, UV-visible, and NIR-IR. Please contact us if you’d like to schedule a consultation or request for a quote on your next project.
WE CAN HELP YOU!
Contact us NOW for sales & expert advice.