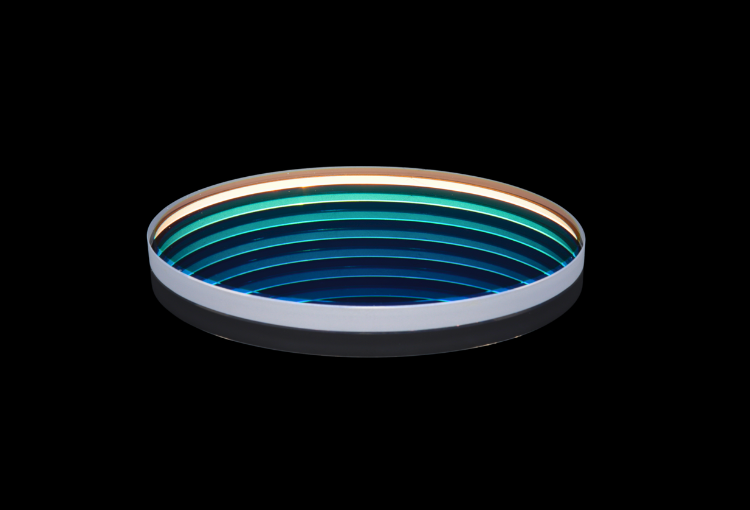
Hot and Cold Mirrors
A cold mirror efficiently transmits infrared wavelengths while reflecting all visible light, whereas a hot mirror reflects infrared wavelengths while transmitting visible light. Both mirrors are used to filter unwanted heat or energy out of a system. They typically use multi-layered dielectric coatings to reflect and transmit light and can be designed for specific wavelength ranges. At Avantier, we produce custom cold and hot mirrors for a wide variety of applications.

Applications
Hot and cold mirrors provide an easy, straightforward way to funnel unwanted heat out of a system. They are used in many different applications where heat generation or the presence of extra IR energy might pose a problem.
Another use of hot and cold mirrors is to overlay two beams. One beam is reflected off the mirror while the other is transmitted through the surface, allowing the mirror to be tilted so that both beams travel along the same path. This is particularly important in surgical lasers, where mirrors are arranged so that a cool, visible laser beam travels along the same path as the invisible hot infrared laser used for cutting tissue. This setup enables the surgeon to see what they are doing.
A UV cold mirror is another type of mirror that reflects UV light while transmitting both infrared and visible light. UV cold mirrors are used in processes where UV light is essential, and the presence of other light would be problematic, such as in the photopolymerization of inks, dyes, and adhesives, or in semiconductor chip manufacturing.
Hot Mirror vs. Cold Mirror Setup
Both mirrors are often used for the same purpose: protecting heat-sensitive equipment from potentially damaging IR radiation. However, since hot mirrors transmit visible light and reflect IR, and cold mirrors reflect visible light while transmitting IR, their placement in a system will differ.
A hot mirror will be placed in the beam path where heat should be removed, usually just before the components that need protection. Visible light will pass through to the heat-sensitive components, while infrared light is effectively blocked.
A hot mirror will be used as a folding mirror in the beam path, as it transmits all the infrared light, effectively eliminating it from the optical system while reflecting visible light.
Factory Standard – Cold Mirrors
Material | Float glass |
Dimensions | +0.5mm |
Thickness | ±0.3mm |
Max temperature | 600 |
Surface Flatness | 3λ per inch |
Surface Quality | 80-50 |
AOI | 45°+/-5° |
Coating | R>95% avg 420-700nm |
R>20% avg 800-2500nm |
At Avantier, we produce custom cold and hot mirrors with a wide range of parameters. We can optimize these mirrors for the desired angle of incidence (0° or 45° are the most common options) as well as for your desired wavelengths and system configurations. If you are looking for cold and hot mirrors for imaging systems, laser systems, or other needs, our designers can work with you to determine what works best for your application. Call us today to set up your initial consultation or place a custom order.
WE CAN HELP YOU!
Contact us NOW for sales & expert advice.