Key Takeaways:
- Optical adhesives are used in optical gluing to bond optical components like lenses and prisms for various functions, such as creating achromatic lenses and complex prism assemblies.
- Key to reliable adhesives are high-precision component processing, dependable adhesive technology, and future advancements like automation. The process involves cleaning, dispensing adhesive, fitting, centering, wiping, UV curing, and inspection.
- Careful alignment of optical components minimizes aberrations and ensures quality.
- Optical adhesives improve performance by reducing reflections and simplifying manufacturing in instruments like cameras and telescopes.
Several key factors contribute to the reliability and performance of optical adhesives. These include the selection of high-precision components, robust adhesive technologies, and the future advancement of your custom optical systems.
- High Precision Processing: High precision in optical gluing is critical for maintaining the integrity of optical components. Alignment accuracy during the fitting and centering stages ensures that the optical paths remain true, minimizing aberrations. Innovations in CNC machining and optical testing methods can enhance the precision of the lenses and prisms before the gluing process begins.
- Reliable Adhesive Technology: Utilizing adhesives that offer superior adhesion properties and thermal stability is essential. Future developments may lead to the creation of new adhesive formulations that resist degradation under varying environmental conditions, thereby enhancing the longevity and performance of glued optical systems.
- Future Enhancements: Continued research into new materials and methods for optical gluing can lead to significant advancements in the field. The implementation of automation in the gluing process has the potential to increase efficiency and consistency, while sensor technologies could provide real-time monitoring of the adhesive curing process.
By focusing on these areas—high precision, reliable adhesives, and future enhancements—Avantier has improved our gluing processes, ultimately resulting in better optical systems that meet the growing demands of advanced applications.
What Are Optical Adhesives?
Optical adhesives, also known as optical cements or optical glues, are substances used to bond two or more optical elements together per specific technical requirements. The optical elements may be lenses, prisms, window pieces, or any number of other parts, and the gluing procedure achieves various optical functions. For example, two multi-order wave plates can be glued together to create a zero-order wave plate. In cases where complex prisms cannot be manufactured as a single piece, multiple prisms can be glued together to enable more intricate optical path conversions. Additionally, the bevel of a right-angle prism can be coated and glued to form a cube, facilitating the creation of a wide-band polarized or unpolarized beam-splitting prism.
Optical gluing is also an essential procedure for achromatic lens groups. Many simple lenses, such as crown or flint glass, exhibit chromatic aberrations; however, by combining a crown glass positive lens with a negative flint glass lens, achromatic effects can be achieved. In achromatic lenses, the positive and negative lens surfaces typically have the same curvature, allowing for precise bonding through optical gluing. Glued lenses offer greater freedom in design than single lenses and can effectively correct other aberrations as well. Correction of spherical aberrations is another example. Compared to assembling two pieces of glass using an air gap, the glued lens assembly simplifies the process and minimizes the impact of lens errors on image quality.
The residual reflectivity of the glued surface is also significantly lower than that of uncoated lenses, simplifying the coating process. In complex optical systems, double- or triple-glued lenses are crucial components for correcting chromatic aberration and improving tolerance sensitivity. They are widely used in various optical instruments, including photographic lenses, micro-objectives, and telescopes. The production of these components relies heavily on the optical gluing process.




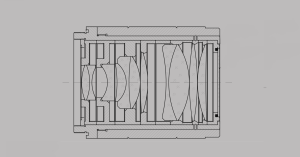
Glued prisms and glued lenses
Processing Steps
The typical steps involved in optical adhesion include lens cleaning, adhesive dispensing, fitting, centering, wiping, curing, and inspection. Here we take the gluing process of lenses as an example:- Lens Cleaning: During the gluing process, it is important to keep the workbench clean and the room temperature stable. Before dispensing the adhesive, the lenses must be wiped perfectly clean to prevent contamination of the adhesive layer. This is also the time to check for any cosmetic defects on the lens and match it according to the center thickness of the lens piece.

- Dispensing: Once the lens is ready, we place a reference lens on the work surface and deposit an appropriate amount of adhesive onto the lens surface (usually with the concave side facing up). The optical glue is colorless, transparent, has high adhesion, and provides excellent transmittance. Various types of adhesives are used for optical gluing, with photosensitive glue being the most common due to its minimal shrinkage, high firmness, thermal stability, and ease of use.

- Fitting: Next, we position the second lens vertically and fit it against the first lens, allowing for free movement until a fringe appears between the two lenses. During this bonding process, we ensure that pressure is applied uniformly and that any air bubbles or excess glue are expelled to maintain an appropriate and uniform adhesive layer thickness.
- Centering: Centering is a critical step in the gluing process. If the optical axes of the positive and negative lenses do not align, it can cause center errors that negatively impact the imaging quality. The optical axes must be recombined with the physical axis of the lens, ensuring that center errors fall within specified limits. This involves using a centering method and conducting eccentricity tests to adjust the lenses as needed.

- Wiping: After centering the lenses, any spilled adhesive is wiped away from the outer edges before formal curing.
- UV Curing: Photosensitive adhesive cures are accomplished under ultraviolet (UV) light. To correct any eccentricity and to clean the lenses, UV lamps should be utilized for curing. It is important to control curing temperature, time, and light intensity strictly during this phase.
- Re-Inspection: After curing, the quality of the glued lenses must be reassessed to ensure that the center error remains within tolerance limits, that the polished surface maintains its finish despite gluing, and that the surface shape meets all testing requirements.
Problems Related to Optical Gluing
One concern in optical gluing involves the adhesive layer’s resistance to laser damage. This resistance refers to the ability of the adhesive to withstand the intensity of lasers without compromising the optical components‘ performance. A careful choice of adhesives can mitigate this problem.
Ready to elevate your optical systems?
Whether you’re seeking to enhance your manufacturing processes, explore the possibilities of achromatic lenses, or delve into the world of complex prism assemblies, understanding the nuances of optical gluing is your first step. Let’s connect and explore how these insights can be applied to your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can help you achieve optical excellence.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!