Key Takeaways
- Underwater imaging technology is vital for marine exploration and research including underwater camera. Conventional wide-angle lenses suffer from distortion and chromatic aberration underwater, degrading image quality.
- An underwater imaging correction lens, with additional lens groups, counteracts these issues, significantly improving image clarity and accuracy.
- This advancement enhances our capacity to observe and study the underwater world, supporting operations in marine industries like archaeology, resource exploration, and environmental monitoring.
Introduction of underwater imaging technology
Underwater imaging is the process of capturing and rendering visual representations of objects within underwater environments through specialized technologies. This enables the quality of underwater cameras, and improved observation and understanding of the underwater world.
Underwater imaging technology is a vital area of research within marine and underwater optics, serving as an essential tool for human exploration, utilization, and conservation of the oceans. Its applications are widespread, including marine resource exploration, underwater archaeology, biological research, underwater engineering installation and maintenance, environmental monitoring, rescue operations, and salvage.

Problems with underwater imaging lenses
Underwater imaging is inseparable from the imaging objective lens, usually a wide-angle lens. Conventional wide-angle lenses are designed for air as the incident medium. When the imaging equipment works underwater, the imaging light of the underwater target passes through the water-window-air and enters the objective lens. In this process, refraction and scattering will be produced, which will bring various aberrations to the imaging system and affect the imaging quality.
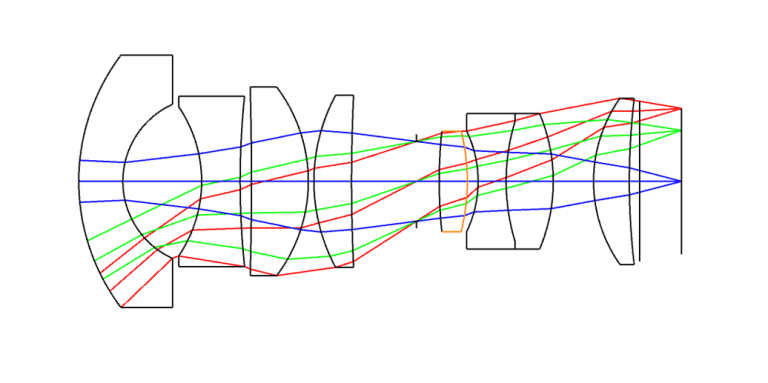
The following is an industrial wide-angle lens by Avantier. This lens is designed for air as the incident medium, and image quality is good. However, when the incident medium is water and a flat glass window is added, image quality is significantly affected.
-768x296.png)
-768x301.png)
- Distortion: When conventional lenses are used for underwater imaging, the edges of the image exhibit significant distortion. While this does not necessarily impair image clarity, it hinders accurate representation of the observed object’s shape, particularly in measurement applications.
- Chromatic aberration: Because water and air have different refractive indices for different wavelengths of light, conventional lenses used directly for underwater imaging can cause serious chromatic aberration.
Furthermore, the interface between the flat window and the water introduces additional aberrations, such as spherical aberration and coma. These distortions are most severe at the edges of the field of view. To achieve optimal underwater imaging results, mitigating these effects is crucial.
Underwater imaging correction lens
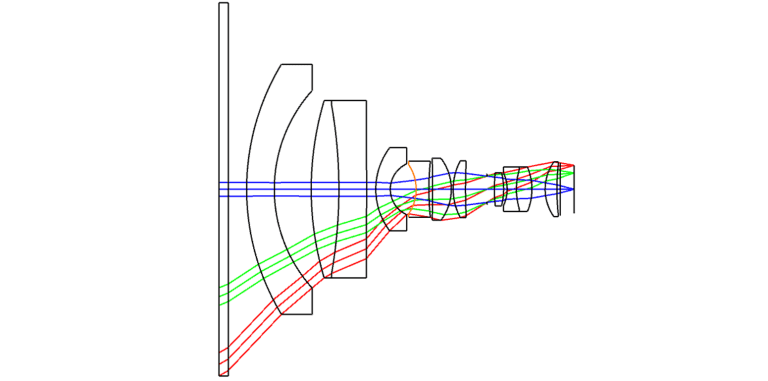
To achieve optimal image quality, aberrations caused by the change in the incident medium must be addressed. A common method is to introduce an additional lens group in front of the primary lens.
This correction lens group resembles a modified telescope design, featuring a very short focal length. By introducing its own controlled distortions, it effectively counterbalances those introduced by the medium change. Additionally, chromatic aberration can be simultaneously corrected through the use of achromatic doublet lenses.
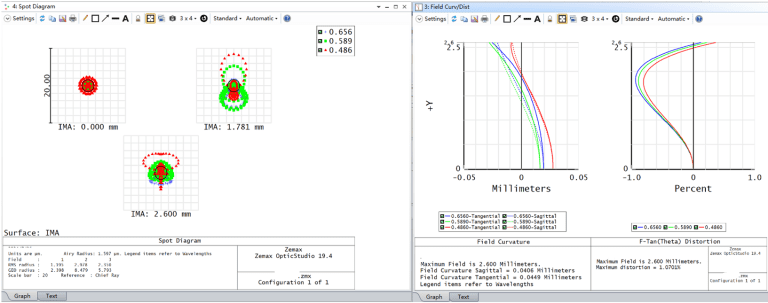
Based on their original wide-angle lens design, Avantier proposed modifying the incident medium to water and adding a lens group consisting of a negative front element and a positive rear element. The optimized design results demonstrate that the distortion and chromatic aberration caused by the medium change are eliminated, while other aberrations are essentially restored to the original design levels. This modified lens is well-suited for underwater photography applications.
Custom Underwater Imaging Lenses
In conclusion, underwater imaging technology is pivotal for advancing marine research and applications. However, conventional wide-angle lenses, when used underwater, present challenges such as distortion and chromatic aberration, which significantly degrade image quality. The development of specialized underwater imaging correction lenses, incorporating additional lens groups to counteract these aberrations, marks a significant advancement. By optimizing the design for the unique refractive properties of water, these correction lenses enable high-quality, accurate images essential for diverse underwater activities, including exploration, archaeology, and environmental monitoring. This innovation not only enhances our understanding of the underwater world but also bolsters critical operations in marine industries.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!







