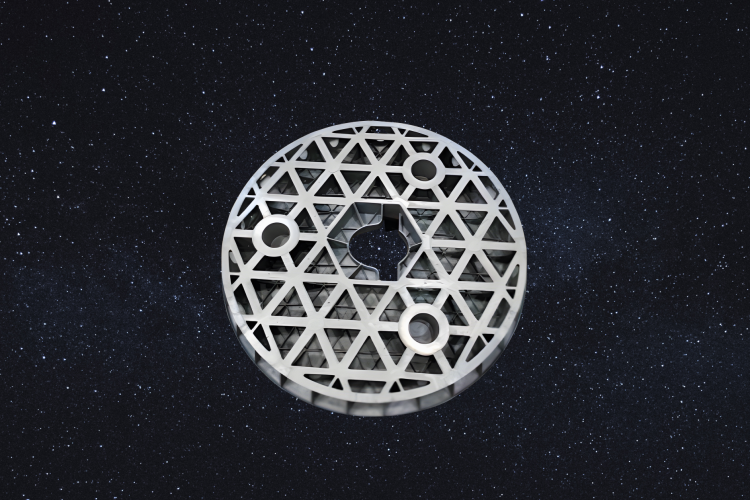
Key Takeaways Unmatched Lightweighting: Achieved a ≤ 40 kg/m² surface density and 90% weight reduction for large-aperture primary mirrors, setting a new benchmark in ultra-lightweight space optics. Superior Material Performance: RB-SiC mirrors outperformed Beryllium in thermal stability and specific stiffness, proving Reaction-Bonded Silicon Carbide (RB-SiC) as the optimal substrate for extreme space environments. AI-Driven Precision […]