Key Takeaways
- LiDAR enables advanced VR experiences by providing precise, real time 3D spatial mapping.
- Once bulky and expensive, modern LiDAR systems are now compact enough to fit into smartphones like the iPhone Pro 12.
- This technology enhances VR/AR experiences with benefits such as better spatial tracking, faster virtual object placement, enhanced realism, and improved depth sensing.
- Key specifications include detection range, range precision, accuracy, field of view, and scan patterns.
- Avantier specializes in designing high precision LiDAR components, enabling customized solutions for AR/VR applications.
LiDAR VR/AR Applications
LiDAR VR/AR applications are taking augmented and virtual reality applications to the next level. Once far to expensive and bulky for consumer applications, today a basic LiDAR system can be condensed to fit into a smart phone and cost less than a hundred dollars. Here we’ll look at just how they work, and what to expect from the combination of LiDAR and AR/VR.

What is LiDAR?
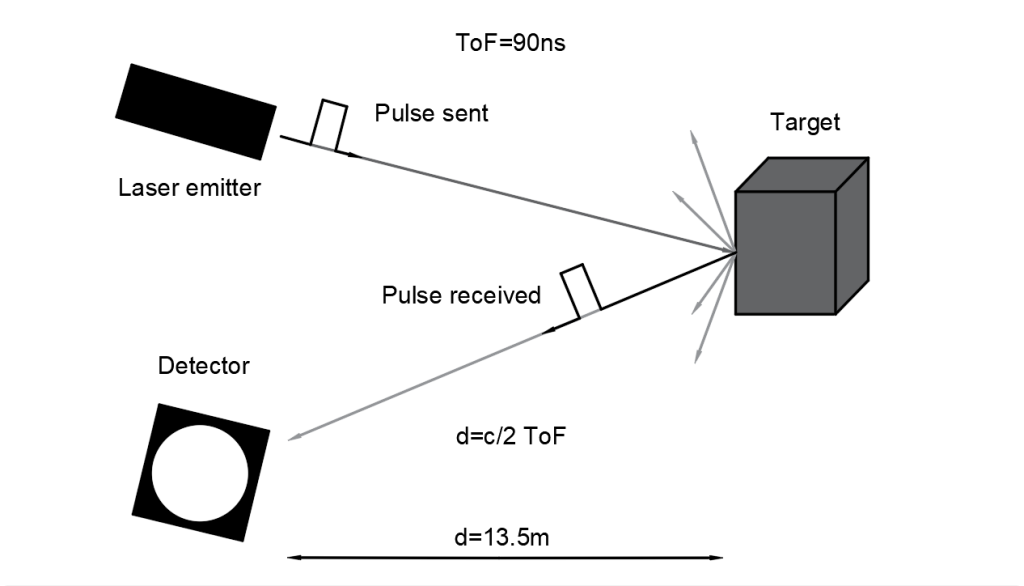
Think of LiDAR as optical radar. An acronym for Light Detection and Ranging, it uses light waves from a laser to create a highly accurate, super-speedy 3D map of an object or area. Wavelength of the laser is typically 250 nm to 11μm but depends on the application requirements.
A quick working sensor makes time of flight (TOF) calculations— determining just how long each laser pulse takes to reach the target and return— and uses this raw data and point clouds to create a precise 3D map of terrain or objects and their placement in space. The intensity of the reflected light can provide extensive information, too, about the type of materials scanned and their density.
LiDAR scanners were originally developed for research purposes, especially meteorology applications. It was successfully used to map the surface of the moon back in 1971, but the technology behind it has improved dramatically and LiDAR today is cheaper, faster, and more powerful than ever before. This new affordability is part of the reason behind the explosion of LiDAR use across real world industries today. We see it in self-driving cars, in speed enforcement, in stormwater management in agriculture— and in AR/VR.
LiDAR and AR
Before the integration of LiDAR with augmented reality, AR was limited by clunky machine vision systems that struggled to provide precise real time 3D mapping. Today, with precise spatial mapping at the speed of light, LiDAR gives AR and VR systems the potential to be faster, more accurate, and so more responsive.

When Apple integrated a miniature LiDAR system into the 2020 iPad Pro and iPhone Pro 12, the power of LiDAR became available to AR and VR app makers for the first time. Since then, they’ve been experimented with extensively. There’s more than one way that augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality systems can be improved by LiDAR integration. A few benefits of the integration include:
- Better Spatial Tracking
- Faster Placement of Virtual Objects
- Enhanced Realism
- Improved Depth Sensing
LiDAR for AR/VR Specifications
Producers of smartphones and AR and VR viewing devices today have the potential to take their viewer’s experience to the next level by incorporating LiDAR technology into their devices. But types and capabilities of LiDAR scanners vary greatly. Here’s a brief summary of some of the most important specs for AR/VR LiDAR.
- The LiDAR Detection Range gives the maximum distance at which LiDAR can detect an object. It is dependent on laser power, laser type, and aperture size. While airborne LiDAR may be used to map surfaces hundreds to thousands of meters away, the types of LiDAR incorporated in consumer devices typically have a much more limited detection range. The iPhone Pro 12’s LiDAR, for instance, can scan at distances up to five meters.
- LiDAR Range Precision tells you just how repeatable measurements will be. If precision is high, multiple measurements of the same object will cluster close to a mean value; but low precision tells you there is significant scatter.
- LiDAR Range Accuracy is like precision, but rather than comparing measurements to each other, it compares them to the actual distance. High accuracy means measurements are very close to the real distance.
- Field of View (FOV) refers to the angle over which the LiDAR system works: either the angle covered by the sensor or that which signals are emitted, whichever is smaller. A mechanically rotating system may have 360 degree field of view, but for many virtual reality applications, a smaller FOV is sufficient.
- Scan Pattern tells you how the laser beam moves to perform its measurement, and includes information like point density and the number of scan lines. In some LiDAR scanners, this may be customizable.
AR/VR LiDAR at Avantier
Avantier is a premier producer of custom high precision optics, including LiDAR components and systems built to our customer’s exact specifications. Our expert engineers and designers are available to help you at any stage of the process, whether you’re doing your initial research or have a custom design ready to go. Contact us today for your next project.
References
- Applied Tech Review. LiDAR Powering Future AR/VR and Metaverse Experiences. May 2024.
- Luetzenburg, G., Kroon, A. & Bjørk, A.A. Evaluation of the Apple iPhone 12 Pro LiDAR for an Application in Geosciences. Sci Rep 11, 22221 (2021).
- Wandinger, Ulla. “Introduction to lidar.” Lidar: range-resolved optical remote sensing of the atmosphere. New York, NY: Springer New York, 2005. 1-18.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!







