Key Takeaways:
- Telecentric lenses ensure consistent magnification and high image quality, minimizing distortion and offering a wide depth of field.
- They excel in precise measurements across varying distances, crucial for quality control in industries like photolithography.
- These lenses are pivotal for capturing detailed, clear images and detecting imperfections that conventional lenses might miss.
- Whether for metrology or long-distance imaging, telecentric lenses provide unmatched reliability and performance in machine vision systems.
Benefits of Telecentric Lenses
Do you need repeatable, high-accuracy measurements? Then maybe you need to fit a telecentric lens to your machine vision system.
When viewed with a telecentric lens, an object will remain exactly the same size, no matter how much it moves around. This is in contrast to more conventional lenses, for which close objects appear much bigger than those farther away. But how does this work, and what all are telecentric lenses good for? Let’s examine those two questions here.
How Telecentric Lenses Work
A telecentric lens is actually a multi-part optical lens assembly designed to eliminate parallax, or perspective error. The figure below illustrates the difference between the field of view of a conventional lens and a telecentric lens: while a conventional lens has an angular field of view, the field of view of the telecentric lens is constant. This means that a telecentric lens has the same field of view at any distance from the lens.
Key Advantages
Advantages of telecentric lenses include:
- Constant magnification
- High image performance
- Low distortion
- Wide depth of field (depending on design of lens)
Telecentric lenses have an important place in machine vision, especially when one might need to take measurements of objects that may be situated at different working distances from the lens. The set of images below illustrates this. Two identical objects are placed at varying distances from the lens position. The first image shows what a conventional lens would see; the second shows the image taken by a telecentric lens. While a conventional lens might offer more useful information about how far away the object, the telecentric lens is what you would choose if you needed to make an accurate measurement under constant magnification.



A telecentric lens eliminates the parallax error caused by the angular field of view of a conventional lens.
But telecentric lenses aren’t just used for measurements or metrology applications. They can also be used to enable long distance cameras to capture clear images, or for any applications where a sharp field of view and high resolution is crucial. They’re also used in photolithography. Let’s look closer at a few specific applications here.
Telecentric Lenses in Quality Control
Machine vision measurements and metrology is one application of telecentric lenses in quality control. But the unique properties of these lenses also enable them to reliably find tiny defects that would be invisible to a more conventional lens. For these applications, teleentric lenses can be coupled with telecentric illumination systems.
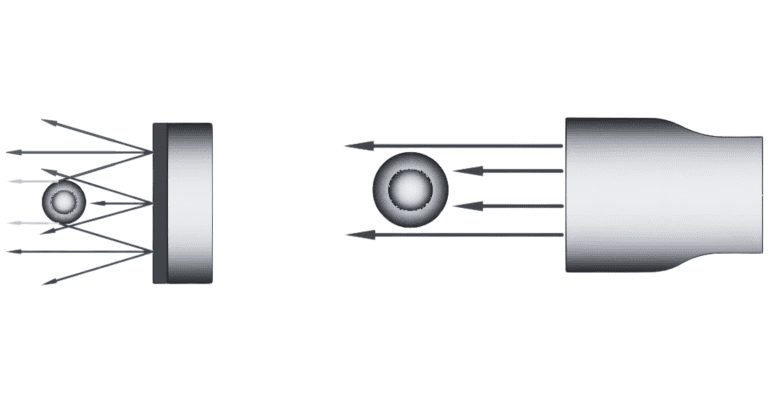
In telecentric illumination, light rays are collimated to be parallel to the optical access. This produces a clear silhouette. While diffuse reflections produce blurred edges when an image is taken with traditional lighting, telecentric illumination and imaging can produce images with sharp, high contrast edges. Thus a telecentric lens can be used to capture an extremely detailed, high resolution image, elucidating any defects in a manufactured part.
Telecentric lenses in Photolithography
Microlithography is another important application of telecentric lenses. This manufacturing technique, often used for manufacturing integrated circuits, uses light to transfer enormous amounts of information to a wafer.
In typical photolithography,the wafer is coated by a light sensitive polymer (the photoresist), which is then exposed to patterned light and developed to form a three dimensional relief image. The exposure to light is achieved through projection printing, and the lithographic projection lens must maintain constant magnification throughout the depth of field. This requires a telecentric lens.
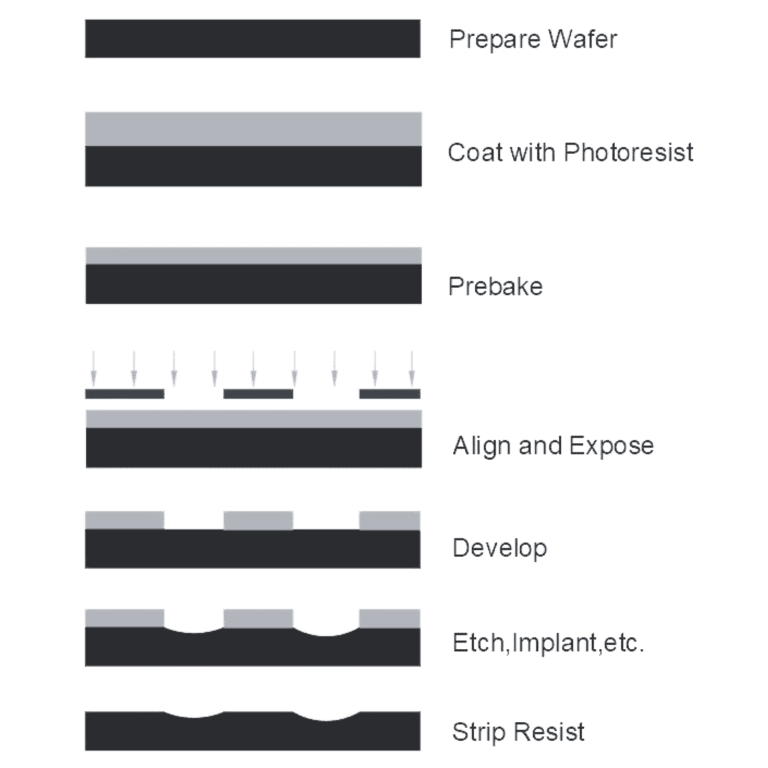
After a photoresist has been exposed, it undergoes further processing, culminating in a stripping of the remaining photoresist. The result is a precisely-manufactured part ready to perform the function for which it was designed.
Telecentric Lenses at Avantier
At Avantier, we produce custom telecentric lenses for a wide variety of clients, in fields ranging from research to industry. Contact us if you’d like to discuss your optical needs or to set up a consultation.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!






