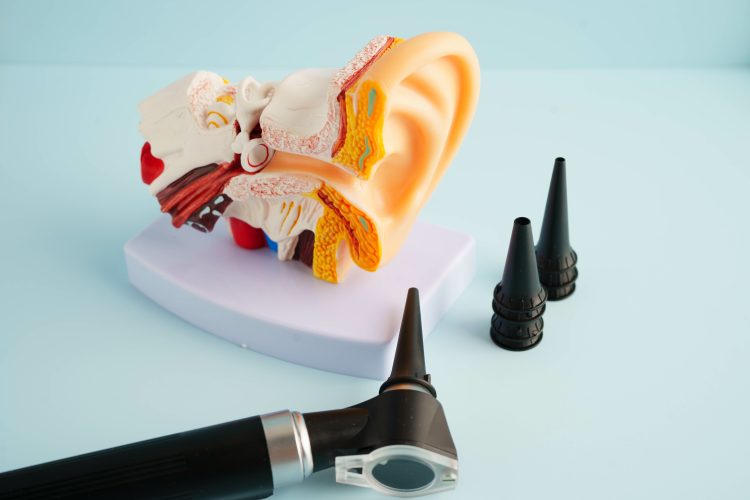
Key Takeaways Medical lens ear endoscopes offer high-resolution visualization for enhanced ear disease diagnosis and treatment. They utilize advanced optical and illumination systems for detailed examination and surgical assistance. Ongoing innovations like 3D imaging and AI integration promise further advances in this critical otolaryngology tool, improving diagnostic accuracy and surgical outcomes. The ongoing evolution of […]