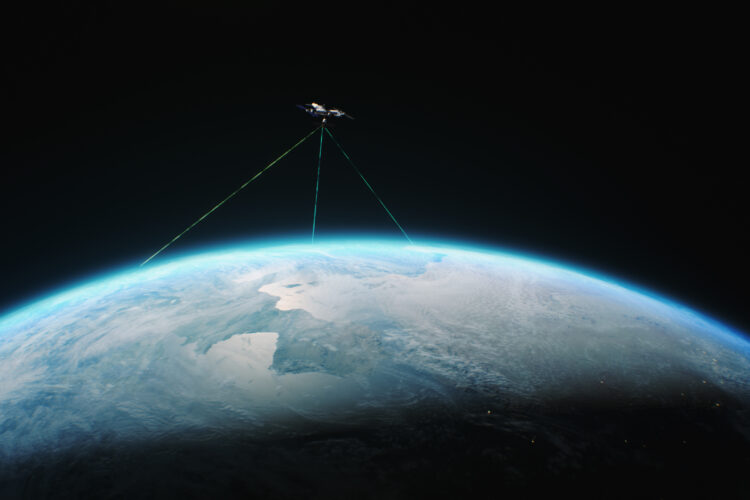
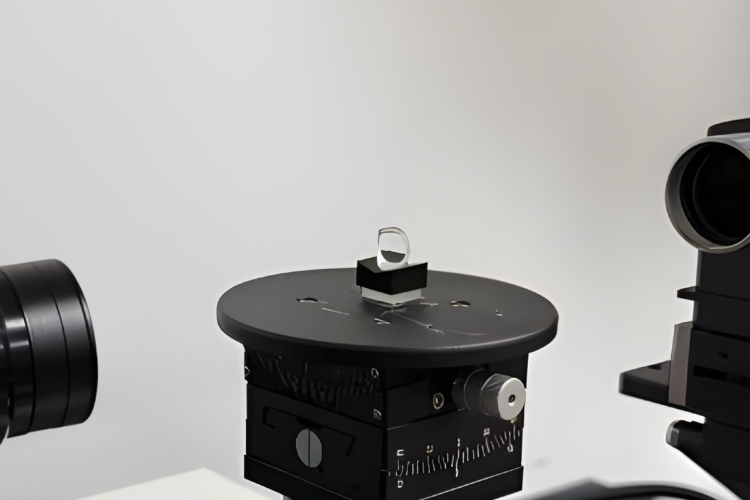
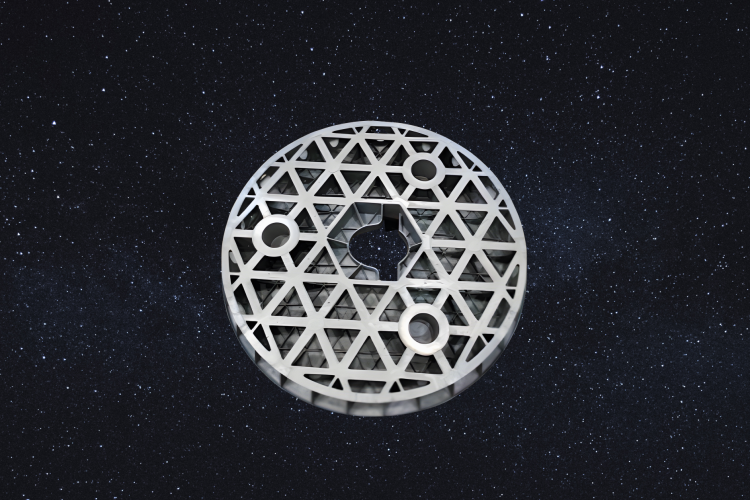
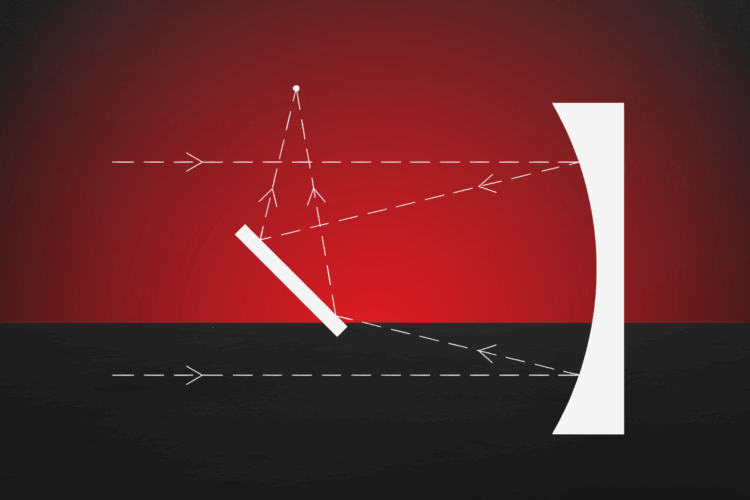
While the fundamental advantages of Free-Space Optical Communication (FSOC)—such as high bandwidth and RF-jamming immunity—are well-established (see our FSOC Fundamentals), the industry is now shifting from “proving the physics” to “optimizing the architecture.”
For aerospace engineers and system architects, the challenge has moved beyond simple Pointing, Acquisition, and Tracking (PAT) to the scalability, manufacturability, and intelligence of the terminals themselves.