Key Takeaways: Eye Lesion Detection Lenses
- Two main types of medical eye lesion detection lenses exist: long-distance and zero-distance. Long-distance lenses are non-contact and safe. They require cooperation and are good for screening adults/adolescents. Zero distance lenses are designed for direct contact, and provide high resolution for infants/uncooperative patients. They do have the potential for discomfort but are crucial for early congenital disease detection like ROP.
- Zero-distance lens design prioritizes infant eye safety with smooth, biocompatible materials and pressure sensors.
- Future advancements aim to improve accuracy and safety for vulnerable populations through interdisciplinary innovation.
Lesion Detection Lens Types
Medical detection lenses designed to identify eye diseases are divided into two types based on optical working distance: long-distance detection lenses and zero-distance detection lenses.
Long-Distance Detection Lens (Approximately 15mm from the Eye)
- Advantages: Non-contact design ensures safety. Detection of lesions is painless, minimizing discomfort, which makes it more acceptable to patients.
- Disadvantages: Requires patient cooperation for accurate detection.
Zero-Distance Detection Lens (In Direct Contact with the Eye)
- Advantages: Specifically designed for infants who may not cooperate during examinations. This is particularly important when detecting congenital eye diseases in newborns, enabling early diagnosis and treatment.
- Disadvantages: Direct contact with the eye may cause discomfort for the patient.
Our Challenge with Eye Lesion Detection Lens
Optical designers at Avantier were asked to design a zero-distance detection lens that would enable safe and reliable diagnostics of lesions in infants as well as other patients. One of the main challenges in this project was the front-end design of the zero-distance detection lens. Given the fragility of an infant’s eye, the front lens element and housing had to be smooth, rounded, and seamlessly integrated. Five design geometries were proposed for the front lens; three were prototyped, tested, and evaluated for safety, manufacturability, and optical performance. We incorporated multiple rounded chamfers on the lens surface to eliminate any sharp edges, ensuring safe contact with the eye. This exposed front element design introduced additional complexity in achieving surface smoothness and edge tolerances. The unique shape of this lens presented manufacturing difficulties, but with multiple iterations to refine the production process we achieved a qualified final product.Initial housing materials were evaluated, including medical-grade stainless steel and titanium alloys. Although stainless steel showed good machinability, it produced internal reflections that caused stray light. After testing, titanium alloy was selected for its balance of biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and optical performance.
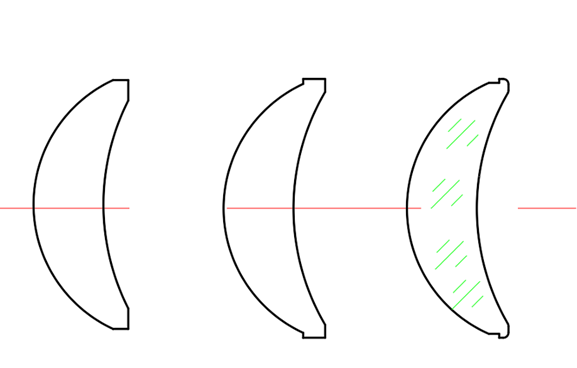
Technical Classification and Design Differences
Eye lesion detection lenses intended for use in different situations will be designed quite differently. Here we consider the technical classification and clinical applications of two very different lenses.
1. Long-Range Detection Lens
- Operational Principle: A non-contact optical system images the eyes from 10-30cm using a telephoto lens (50-100mm), relying on high-speed autofocus (AF) technology to compensate for the patient’s small movements. Typical devices, like a handheld wide-angle fundus camera, can cover a 130° range of the retina.
- Technological Superiority: The procedure is painless, making it suitable for routine screening of adolescents and adults. Automated grading of diabetic retinopathy has an accuracy of over 92%.
- Boundedness: The imaging resolution of an infant’s eyeball (approximately 16mm in diameter) may be insufficient, and small lesions (such as threshold lesions of retinopathy of prematurity) can easily be missed.
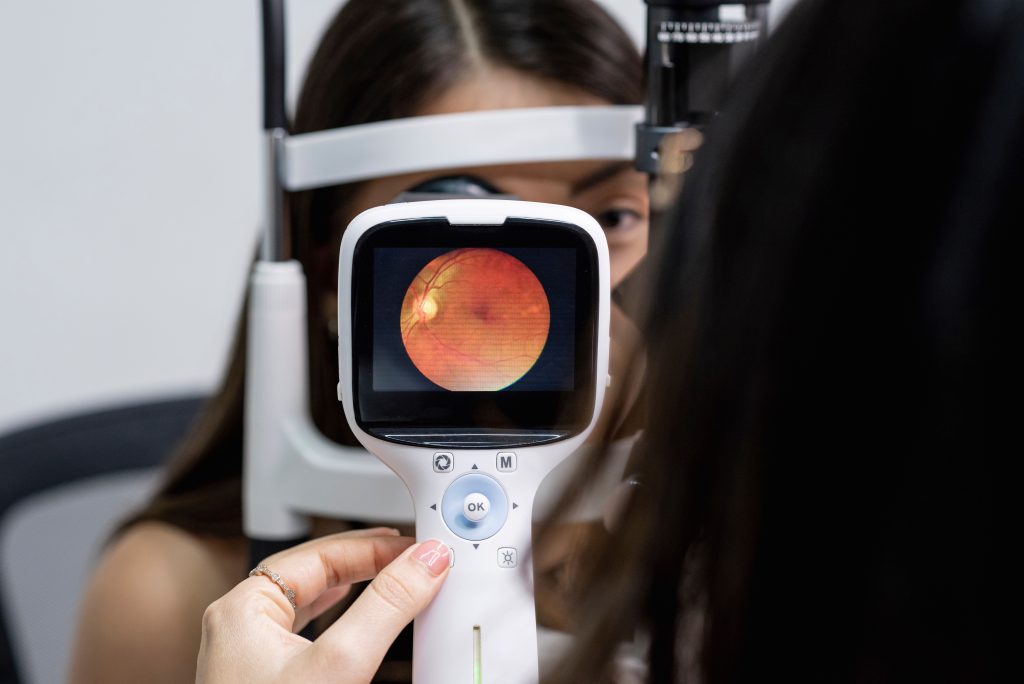
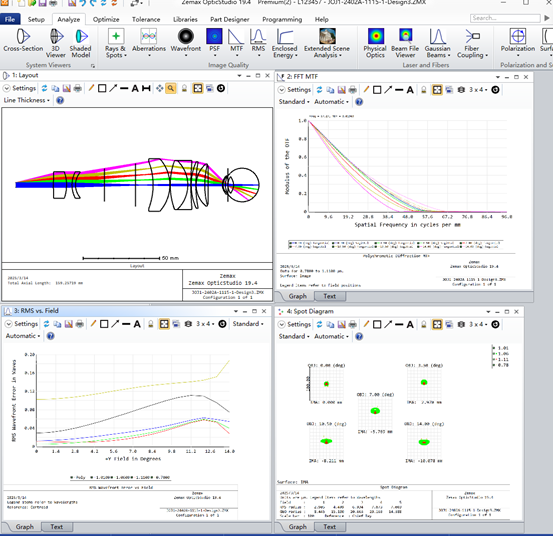
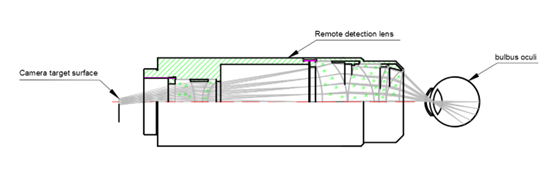
2. Zero-Distance Detection Lens
- Operational Principle: A 0-5mm diameter probe with a miniature optical lens is required to gently touch the cornea or sclera. This shortens the distance to 0.1-0.5mm, improving resolution to the cellular level (<2μm). A typical representative is the neonatal scleral compression OCT probe. – Core Design Breakthroughs:
- Biocompatible Materials: The probe is wrapped in medical silicone gel to prevent scratching of the cornea. Material selection also required evaluation for dimensional stability, internal stress behavior, and biocompatibility under thermal variation.
- Dynamic Pressure Sensing: A built-in microforce sensor (range 0-5N) helps prevent increased intraocular pressure.
- Rapid Sterilization Module: The detachable probe supports a 60-second UV sterilization cycle to avoid cross-infection.
- Applicable Population: Primarily used for preterm infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and children with cerebral palsy who are unable to open their eyes.
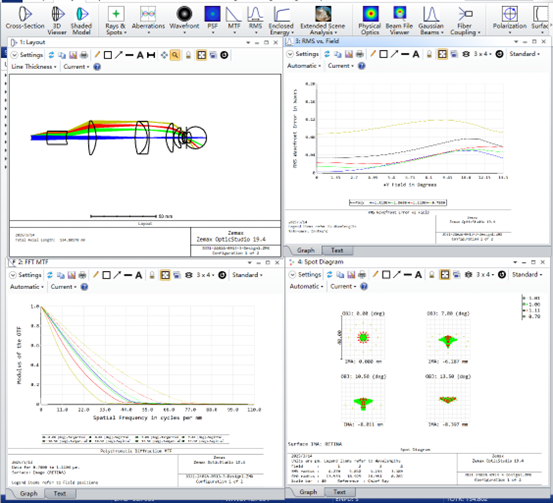
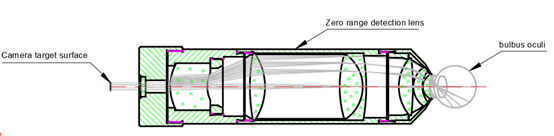
Comparison of Clinical Application Scenarios
1. Routine Screening Value of Long-Distance Lenses
– Scenario 1: School Eye Health Survey
The portable wide-angle lens can complete monocular imaging within 5 seconds. When combined with cloud AI diagnostics, the detection rate of refractive errors and conjunctivitis reaches 85%.
– Scenario 2: Emergency Eye Trauma Assessment
Non-contact features make it safe for use in patients with open eye injuries, effectively identifying occult scleral fissures via near-infrared imaging (sensitivity 91%).
2. Special Group Application of Zero-Distance Lenses
– Scenario 1: Retina Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) Screening
Conventional indirect ophthalmoscopy requires forced opening of the infant’s eyelids, leading to a misdiagnosis rate of up to 30%. The zero-distance OCT probe can non-invasively display the retinal vascularization boundary, increasing the accuracy of ROP staging to 97% (data from the National Eye Institute).
– Scenario 2: Diagnosis of Congenital Glaucoma
The anterior chamber angle and optic cup shape are measured using the compression probe, combined with the intraocular pressure sensor (precision of ±0.5mmHg).
Comparative safety analysis
Risk indicator | Long distance lens | Zero distance lens |
|---|---|---|
Risk of infection | 0% (noncontact) | 0.03% (Sterilization Failure Case) |
Mechanical damage probability | 0% | 0.1% (caused to operation error) |
Data error rate | 12% (mobile artifact) | 4% (near eliminate motion blur) |
The Future of Eye Lesion Detection Lenses
The differences between long-distance and zero-distance detection lenses reflect the evolutionary trend of medical equipment from “universality” to “accurate group adaptation”. Although zero-distance technology still faces controversy, its irreplaceability in the prevention and treatment of infant eye disease has been widely accepted. In the future, we anticipate that cross-innovation between materials science, artificial intelligence, and medical workers will improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce operational risks, enabling us to build a safer diagnosis and treatment system for vulnerable groups. If you are looking for high quality eye lesion detection lenses, contact Avantier today.