Key Takeaways
- Medical lens ear endoscopes offer high-resolution visualization for enhanced ear disease diagnosis and treatment.
- They utilize advanced optical and illumination systems for detailed examination and surgical assistance.
- Ongoing innovations like 3D imaging and AI integration promise further advances in this critical otolaryngology tool, improving diagnostic accuracy and surgical outcomes.
The ongoing evolution of medical technology has positioned endoscopy as a critical tool for minimally invasive exploration of internal anatomical structures, providing invaluable diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities. Functioning as a direct visualization modality, endoscopy overcomes limitations inherent in indirect imaging techniques, enabling the detection of subtle pathologies. In recent years rigid and flexible lens-based ear endoscopy has emerged as an indispensable modality for the diagnosis and management of otologic disorders.
Fundamental Principles of Lens-Based Ear Endoscopy
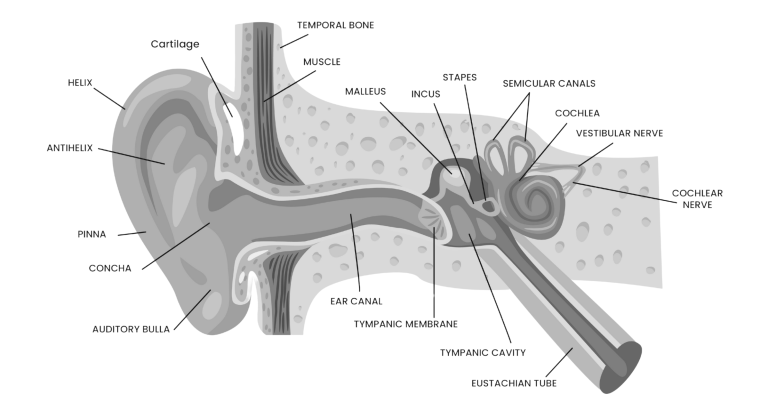
Lens-based ear endoscopes are specialized optical instruments designed for detailed examination of the external auditory canal (EAC), tympanic membrane (TM), and middle ear. The intricate anatomy of these regions, encompassing the EAC, TM, and ossicular chain, often precludes direct visualization and necessitates advanced imaging techniques. The advent of high-resolution, small-diameter endoscopes has revolutionized otolaryngology by providing clinicians with direct, magnified views of these structures, facilitating enhanced diagnostic accuracy and targeted therapeutic interventions.
Operational Mechanisms of Lens-Based Ear Endoscopes
(I) Optical Imaging Principles:
Modern ear endoscopes leverage miniaturized, high-definition camera systems integrated at the distal tip. These optical assemblies typically incorporate multi-element lens stacks engineered for optimal resolution, depth of field, and field of view within the confined dimensions of the ear canal. Illumination is provided via integrated light sources, and reflected light from the target tissue is captured by the image sensor (e.g., CMOS or CCD). The resulting analog signals are then processed and converted into digital video signals for real-time display on a monitor. Advanced systems often employ digital image processing algorithms to enhance image clarity, color fidelity, and contrast, aiding in the differentiation of normal and pathological tissues.
(II) Illumination Systems:
Effective illumination within the narrow and often obstructed ear canal is paramount for high-quality visualization. Current generation ear endoscopes predominantly utilize cold light sources, such as high-intensity LEDs, coupled with fiber optic light guides for efficient and safe light delivery to the distal tip. This design minimizes thermal output at the tissue interface, mitigating the risk of iatrogenic thermal damage to delicate otologic structures. Advanced illumination techniques, such as narrow-band imaging (NBI), are increasingly being integrated to enhance the visualization of vascular patterns and mucosal abnormalities based on differential light absorption characteristics.
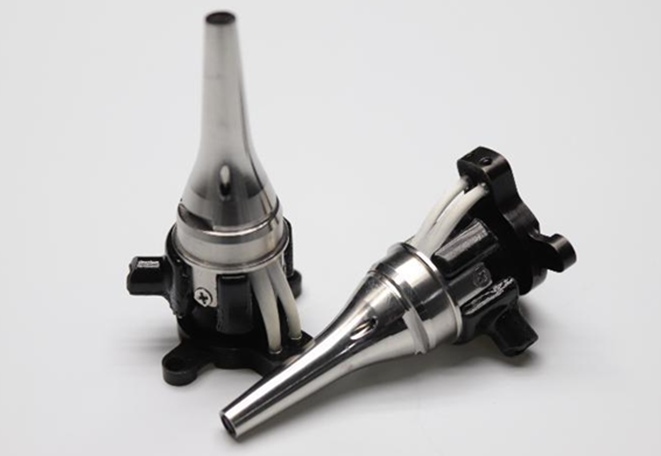

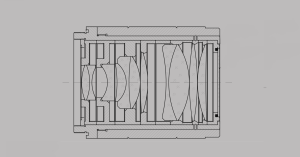
The miniaturization of optical components presents significant engineering challenges. Achieving high optical transmission and resolution with internal lens diameters of merely 2.7mm, as in these Avantier ear endoscopes, necessitates sophisticated lens design and fabrication processes.

Clinical Applications of Lens-Based Ear Endoscopy in Otologic Diagnosis and Treatment
Lens-based ear endoscopes are important in both diagnosis and treatment. Here is a summary of some important applications.
(I) Diagnostic Applications:
- External Otitis: High-resolution endoscopy allows for detailed visualization of the entire EAC, enabling precise identification of inflammatory changes (erythema, edema), skin lesions, debris, and the presence of cerumen impaction or foreign bodies. in external otitis, the endoscope facilitates direct observation of canal wall thickening and exudate. In cases of cerumen impaction, the endoscope provides critical information regarding the location, size, and consistency of the obstruction, guiding appropriate removal techniques.
- Tympanic Membrane Examination: Endoscopic examination provides a magnified view of the TM, making possible assessment of its integrity, color, contour, and mobility. Subtle changes indicative of middle ear pathology, such as hyperemia, perforation (including size and location), or retraction pockets, are readily visualized. This enhanced visualization improves diagnostic accuracy compared to traditional otoscopy.
- Middle Ear Diagnostics: In select cases, particularly following tympanic membrane perforation or during surgical exploration, rigid endoscopes can be introduced into the middle ear to directly visualize the ossicular chain, middle ear mucosa, and identify pathological entities such as ossicular fixation, erosion, or cholesteatoma. This may provide critical intraoperative information for surgical planning and execution.
(II) Therapeutic Applications:
- Cerumen and Foreign Body Removal: Endoscopic guidance facilitates the safe and precise removal of impacted cerumen or foreign bodies from the EAC using specialized micro-instruments introduced through an integrated working channel or alongside the endoscope. Direct visualization minimizes the risk of trauma to the ear canal and tympanic membrane.
- Endoscopic Ear Surgery: Lens-based endoscopes are increasingly employed as adjuncts or primary visualization tools in various otologic surgical procedures, including tympanoplasty, cholesteatoma surgery, and stapedotomy. The enhanced visualization afforded by the endoscope allows for more precise tissue manipulation, reduced surgical morbidity, and improved surgical outcomes.
- Postoperative Monitoring: Endoscopic examination is valuable for postoperative assessment of the surgical site and can be used to ensure graft integrity, identify potential complications, and monitor healing.

Comparative Analysis with Other Endoscopic Modalities
Otic endoscopes exhibit distinct design and performance characteristics compared to endoscopes used in other anatomical systems (e.g., gastrointestinal, urological). The confined and delicate nature of the ear necessitates a significantly smaller diameter of the endoscope shaft, typically in the millimeter range, to facilitate atraumatic insertion into the narrow ear canal. Furthermore, the critical role of the auditory system demands superior optical resolution and illumination to visualize subtle pathological changes that can significantly impact hearing function. Consequently, otic endoscopes often incorporate more sophisticated optical and illumination systems. The design of working channels in otic endoscopes prioritizes compatibility with micro-instruments required for intricate diagnostic and therapeutic maneuvers within the limited surgical space of the ear.

Future Directions and Technological Advancements in Ear Endoscopy
The field of ear endoscopy continues to advance rapidly. Emerging technologies include the integration of three-dimensional (3D) imaging modalities and variable magnification capabilities, providing a more comprehensive and spatially accurate visualization of otologic structures. Future developments are anticipated in the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered image analysis algorithms for automated detection and characterization of ear pathologies, potentially enhancing diagnostic efficiency and accuracy. Advances in biocompatible materials science are also expected to yield more flexible and atraumatic endoscope designs, improving patient comfort during examinations and procedures. These ongoing innovations hold significant promise for further revolutionizing the diagnosis and treatment of ear diseases.
We provide outstanding engineering services for the optical components involved in otoscopic endoscopy. Contact us to discuss your next project.
Related Content
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!