Key Takeaways
- A powell lens is known as laser line generating lens, producing straight, uniform laser lines by expanding collimated beams in one dimension.
- Each lens’s apex showcases an acylindrical curve that evenly redistributes the optical power of a Ø0.
- A Powell lens transforms a Gaussian beam profile into a cross section with a significantly more uniform intensity distribution compared to a traditional cylindrical lens, reducing the central hot spot.
Introduction to the Powell Lens
A laser is a common optical device, widely used in laser communication, medical equipment, lighting, laser printing and other fields. In practical applications, it is sometimes necessary to adjust the laser, such as changing the shape of the laser or adjusting the light intensity distribution. This operation is called laser shaping. The Powell prism is a common laser shaping optical element, designed to convert a circular light spot into a linear light spot and change the light intensity distribution. This process transforms the Gaussian distribution of light into a uniform energy beam, also known as flat-top light.


A Powell lens is actually a cylindrical lens with an aspherical surface, meaning one direction of the surface has an aspherical distribution, while the perpendicular direction has no curvature. Light entering the Powell lens converges and diffuses in one direction, while the length of the spot in the other direction remains the same. In the direction of convergence and diffusion, the degree of deflection of light rays at different entry pupil heights varies, enabling the redistribution of light rays. Although ordinary cylindrical lenses can also output linear beams, they cannot change the light intensity distribution. When a Gaussian beam passes through ordinary cylindrical lenses, the resulting linear beam has strong energy in the middle that gradually decreases away from the center, resulting in poor uniformity.
In addition to generating uniform linear beams, the Powell lens can also be used with other components to achieve different laser shaping effects. For example, two Powell prisms placed vertically can transform a circular spot into a square spot. Powell prisms have important applications in biomedicine, automotive assembly, and food processing.
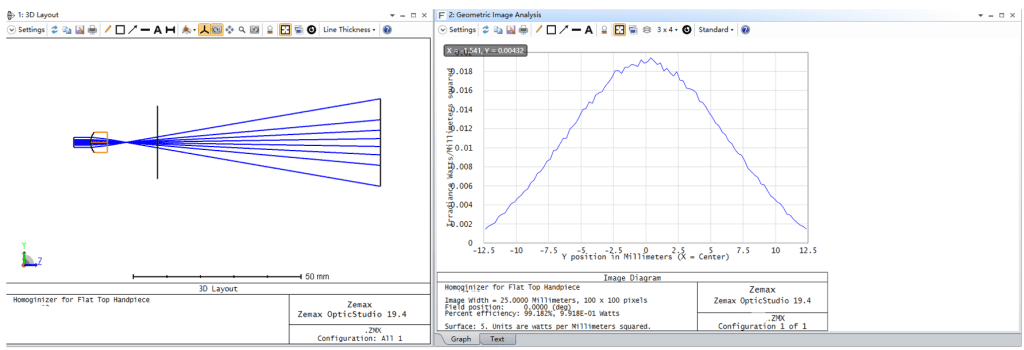
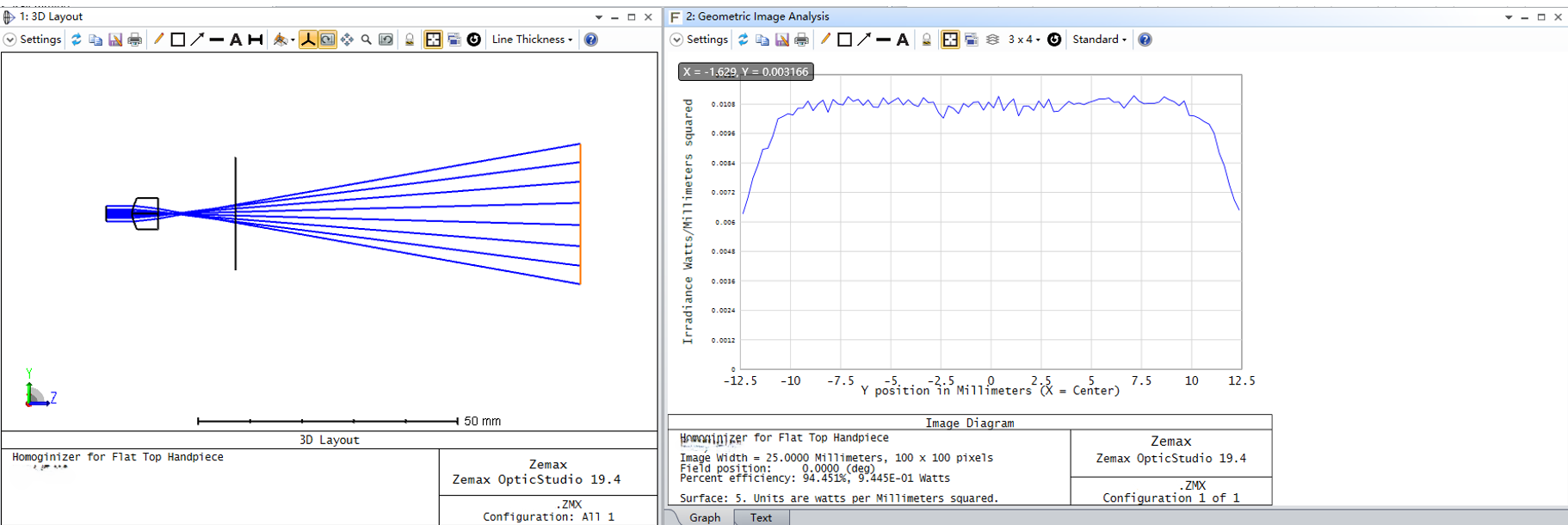
Indicators of Powell Prism
Two main indicators affect the design of Powell prism: fan angle and incident spot size.
The fan angle refers to the angle of the light beam when it passes through the Powell lens and opens into a fan. It is obvious that the larger the fan angle, the longer the length of the linear beam obtained at the same distance.
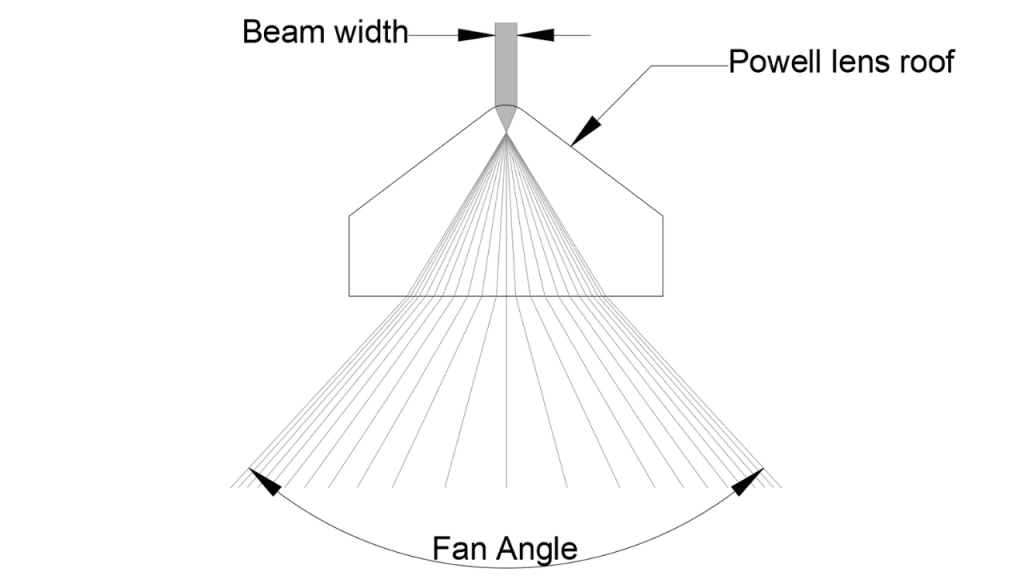
The size of the incident light spot is another important indicator that affects the design of Powell lens. For a laser with a Gaussian distribution, the incident spot size refers to the spot diameter when the energy drops to a peak of 1/e2. In general, specific Powell prisms are only suitable for incident beams of the corresponding size. If the size of the beam is not matched, the energy distribution of the outgoing beam will be significantly affected.
Applications of Powell Lenses
- Machine Vision: Powell lenses are widely used in machine vision applications such as product defect detection, dimensional measurement and alignment.
- Flow Cytometry: Powell lenses are used in flow cytometry instruments used to measure the size and shape of cells and particles.
- Laser Printing: Powell lenses are used in laser printing machines to produce high quality barcodes and other markings.
- Optical Measurement: Powell lenses are used in optical measurement instruments used to measure the smoothness and roughness of surfaces.
Understanding Powell Lens Specifications
Each Powell lens has a specific fan angle. This angle tells you how wide an angle the original beam is fanned out over. It is fully determined by the roof angle of the Powell lens and the index of refraction of the substrate. The performance of these lenses is sensitive to the laser beam width, and for ideal results you will want to use a Powell lens with a roof curvature designed for your specific laser width. While these lenses are both powerful and flexible, they must be manufactured to a high standard, as both the straightness and aperture deviation of the resulting line depends on the quality of the prism. The Powell lens must also be designed with an apex angle that matches the laser linewidth of the application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Powell lenses are indispensable tools in optical engineering, offering precise control over laser beam shaping and intensity distribution. Their unique ability to convert Gaussian beams into uniform laser lines finds critical applications across industries like laser communication, medical devices, and manufacturing. By effectively eliminating central hot spots and ensuring consistent energy distribution, Powell lenses enable enhanced performance in tasks ranging from high-precision measurements to advanced laser processing. As technology advances, their role in shaping light will continue to evolve, driving innovations in fields where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!