Key Takeaways
- Optical coatings, including High Reflective Coatings and dielectric coatings, are thin films applied to optical components to control their reflectance and transmittance properties.
- These coatings work by interfering with light waves, resulting in constructive or destructive interference depending on the coating thickness and the wavelength of light.
- Metallic coatings, such as High Reflective Coatings, offer high reflectance over a wide range of wavelengths, while dielectric coatings provide lower reflectance but can be tailored to specific wavelengths.
- Optical coatings find widespread applications in various industries, including lasers, telescopes, cameras, and medical devices, due to their ability to enhance optical performance.
High Reflective Coatings
Optical coatings are thin films that are applied to optical components to control their reflectance, transmittance, or polarization properties. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including lasers, telescopes, cameras, and medical devices.
How Optical Coatings Work
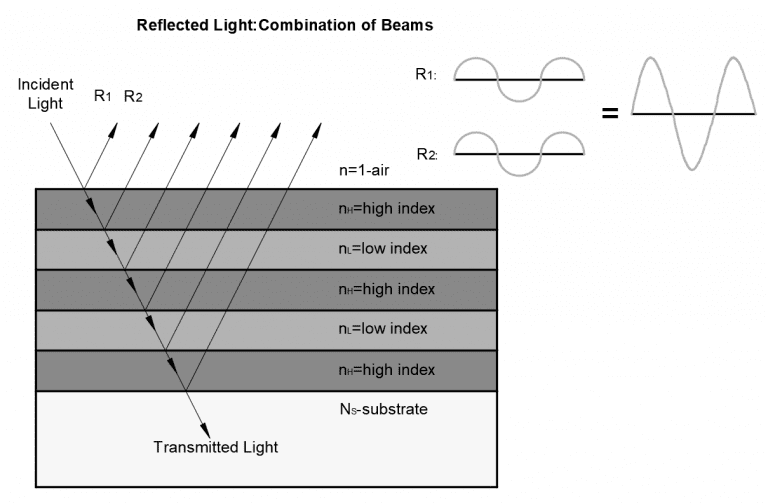
Optical coatings work by interfering with the light waves that are reflected or transmitted by the optical component. When light waves are reflected from a surface, they can interfere with each other constructively or destructively. Constructive interference occurs when the waves are in phase with each other, and destructive interference occurs when they are out of phase with each other.
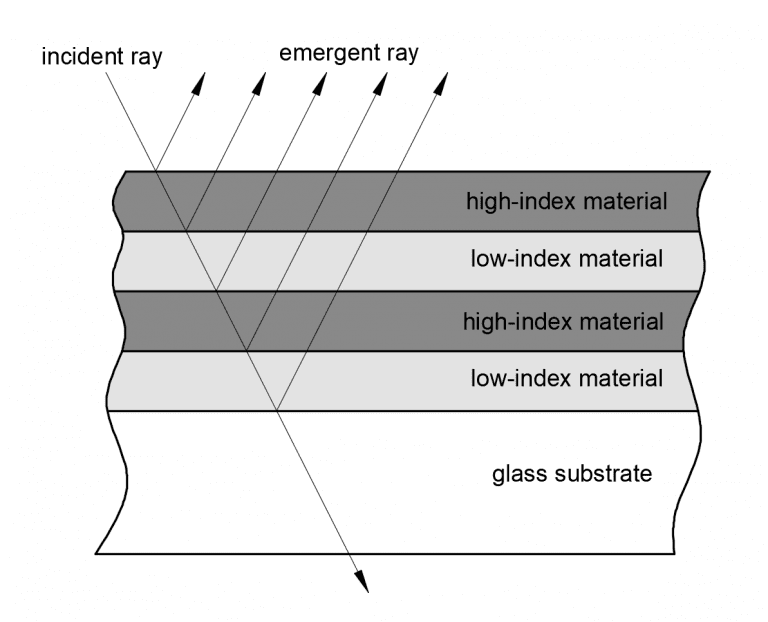
The type of interference that occurs depends on the thickness of the coating and the wavelength of the light. If the thickness of the coating is a quarter of the wavelength of the light, then the waves will interfere constructively, resulting in high reflectance. This is known as a quarter-wave coating.
Types of Optical Coatings
There are two main types of optical coatings: metallic coatings and dielectric coatings.
- Metallic coatings are made of metals such as aluminum, gold, or chromium. They have high reflectance over a wide range of wavelengths. Metallic coatings are used in mirrors, neutral density filters (ND filters), and other applications where high reflectance is required.
- Dielectric coatings are made of materials such as titanium dioxide, tantalum pentoxide, and silicon dioxide. They have lower reflectance than metallic coatings, but they can be designed to reflect or transmit specific wavelengths of light. Dielectric coatings are used in anti-reflection coatings, filters, and other applications where precise control of light is required.
Applications of Optical Coatings
Optical coatings are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Lasers: They are used in lasers to increase the reflectance of mirrors and other optical components. This helps to improve the efficiency of the laser and to reduce losses.
- Telescopes: They are used in telescopes to improve the transmission of light and to reduce glare. This helps to improve the image quality of the telescope.
- Cameras: They are used in cameras to improve the image quality by reducing glare and reflections. They are also used to correct for chromatic aberration, which is a distortion of the image that is caused by the different wavelengths of light being refracted by the lens at different angles.
- Medical devices: They are used in medical devices such as microscopes and endoscopes to improve the image quality and to protect the patient from harmful radiation.
Custom Optical Coatings
Optical coatings can be customized to meet the specific requirements of an application. For example, a mirror for a laser might require a coating that has high reflectance at a specific wavelength. Or, a telescope might require a coating that has high transmission in a specific wavelength range.
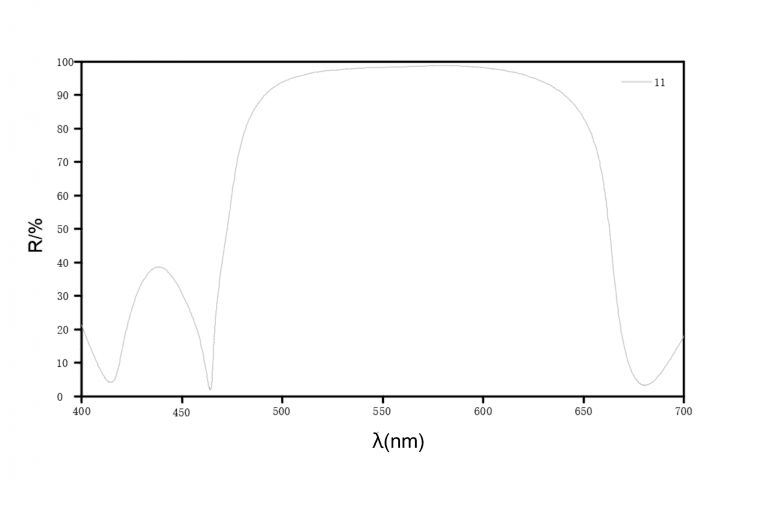
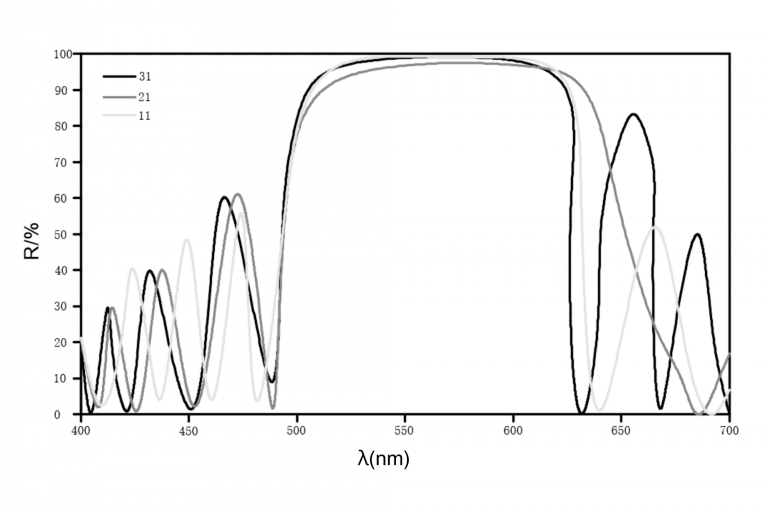
For example, Figure 3shows the reflectance when the number of layers is 11 when HR coating is applied so that the optical film thickness is λ/4 (λ = 550 nm). Figure 4 shows that as the number of layers is increased, the reflectance approaches 100%. At a wavelength of 550 nm, the reflectance of 11, 21, and 31 layers is 98%, 99.9%, and 99.999%, respectively.
The Future of Optical Coatings
Optical coatings are a rapidly evolving field. New coating materials and coating techniques are being developed all the time. This is leading to new and improved applications for the coatings. In the future, optical coatings are likely to play an even more important role in a wide variety of technologies. To discuss your next project, contact us or request a quote! Our expertise in coating technologies and coating design can help you achieve high-performance optical surfaces for your specific needs. Please contact us if you’d like to schedule a consultation or request for a quote on your next project.
GREAT ARTICLE!
Share this article to gain insights from your connections!




